Хотя быстрое прототипирование остается наиболее распространенным использованием аддитивного производства, его наиболее применимой и высокоценной областью является прямое производство функциональных деталей конечного использования. Этот переход от моделей к критически важным компонентам наиболее заметен в таких отраслях, как аэрокосмическая и медицинская, где уникальные преимущества 3D-печати — а именно сложная геометрия и индивидуализация — обеспечивают ценность, которую традиционное производство не может легко воспроизвести.
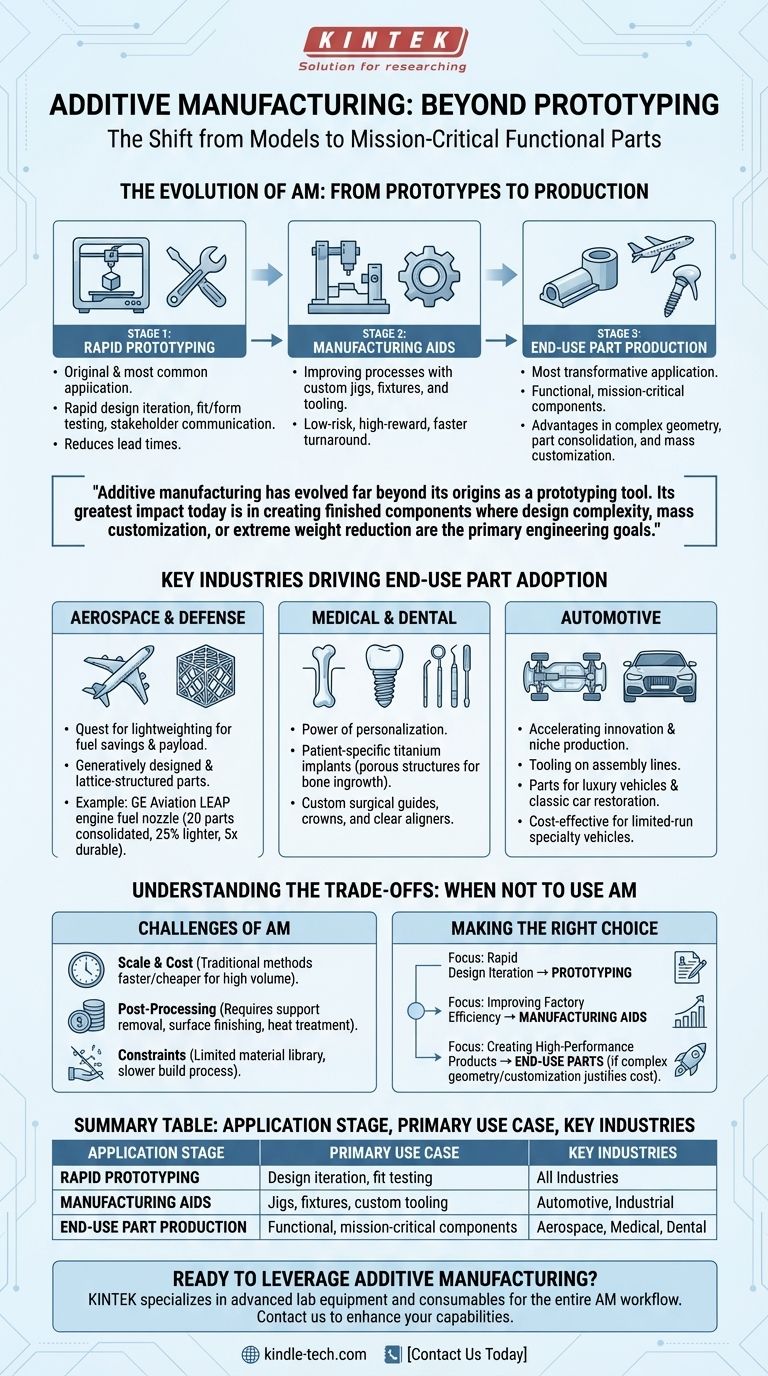
Аддитивное производство значительно эволюционировало за пределы своего первоначального назначения как инструмента для прототипирования. Его наибольшее влияние сегодня заключается в создании готовых компонентов, где основными инженерными целями являются сложность конструкции, массовая индивидуализация или экстремальное снижение веса.

Эволюция АП: от прототипов к производству
Аддитивное производство (АП), или 3D-печать, не стало производственной технологией в одночасье. Его применение развивалось поэтапно, каждый этап основывался на предыдущем.
Основа: Быстрое прототипирование
Это оригинальное и до сих пор наиболее распространенное применение АП. Десятилетиями инженеры использовали 3D-принтеры для быстрого создания физических моделей цифровых проектов.
Ценность проста: это позволяет быстро итерировать дизайн, тестировать посадку и форму, а также общаться с заинтересованными сторонами задолго до того, как приступить к дорогостоящему оснащению для массового производства.
Мост: Производственные вспомогательные средства
Следующим логическим шагом стало использование АП для улучшения самого производственного процесса. Это включает печать приспособлений, оснастки и другого нестандартного инструментария.
Это применение является низкорисковым, высокодоходным входным пунктом для многих компаний. Изготовление нестандартного приспособления, которое могло занять недели, часто может быть напечатано за ночь, что значительно сокращает сроки выполнения и затраты на заводе.
Вершина: Производство деталей конечного использования
Это наиболее преобразующая область применения. Здесь напечатанная деталь не является моделью или инструментом — это конечный продукт, поставляемый заказчику.
Это возможно только тогда, когда АП обеспечивает явное преимущество перед традиционными методами. Эти преимущества обычно делятся на три категории: сложная геометрия, консолидация деталей и массовая индивидуализация.
Ключевые отрасли, стимулирующие внедрение деталей конечного использования
Некоторые отрасли быстро осознали производственный потенциал АП, потому что их потребности идеально соответствуют его сильным сторонам.
Аэрокосмическая и оборонная промышленность: Стремление к снижению веса
В авиации каждый сэкономленный грамм веса напрямую приводит к экономии топлива или увеличению полезной нагрузки в течение всего срока службы самолета.
АП позволяет инженерам создавать генеративно спроектированные и решетчатые детали, которые невозможно изготовить традиционными методами, но которые обладают невероятным соотношением прочности к весу.
Известным примером является топливная форсунка двигателя GE Aviation LEAP. АП позволило дизайнерам объединить 20 отдельных компонентов в одну сложную деталь, которая на 25% легче и в пять раз долговечнее.
Медицина и стоматология: Сила персонализации
Нет двух одинаковых человеческих тел, что делает медицину идеальной областью для возможностей индивидуализации АП.
Хирурги-ортопеды используют АП для создания индивидуальных титановых имплантатов, таких как вертлужные впадины, с пористой структурой, которая способствует врастанию кости. Стоматологи и ортодонты печатают миллионы индивидуальных хирургических шаблонов, коронок и прозрачных элайнеров.
Автомобильная промышленность: Ускорение инноваций и нишевое производство
Автомобильная промышленность широко использует АП для прототипирования новых конструкций транспортных средств. Однако это также ключевой фактор для оснастки на сборочных линиях и производства деталей для роскошных автомобилей и реставрации классических автомобилей.
Для крупносерийного производства АП все еще слишком медленно, но для мелкосерийных специализированных транспортных средств оно обеспечивает экономически эффективный способ создания сложных деталей без дорогостоящего оснащения.
Понимание компромиссов: Когда не следует использовать АП
Для эффективного применения АП крайне важно понимать его ограничения. Это мощный инструмент, но он не подходит для любой работы.
Проблема масштаба и стоимости
Для производства тысяч одинаковых, простых деталей традиционные методы, такие как литье под давлением или фрезерование с ЧПУ, почти всегда быстрее и дешевле в расчете на одну деталь. Основная стоимость АП заключается во времени работы машины и материале, а не в оснастке.
Реальность постобработки
Детали редко выходят из принтера готовыми к использованию. Они часто требуют удаления опорных конструкций, чистовой обработки поверхности, термообработки или других этапов для соответствия окончательным спецификациям. Эти этапы постобработки увеличивают время и стоимость рабочего процесса.
Ограничения материалов и скорости
Хотя библиотека материалов, совместимых с АП, растет, она все еще составляет лишь часть того, что доступно для традиционного производства. Кроме того, послойное создание деталей является по своей сути более медленным процессом на одну деталь, чем штамповка или формовка.
Правильный выбор для вашей цели
"Наиболее применимой" областью АП является не столько важной, сколько правильное применение для вашей конкретной цели.
- Если ваша основная цель — быстрая итерация дизайна: Прототипирование — ваше ключевое применение. Используйте его, чтобы быстро ошибаться, быстро учиться и совершенствовать свой дизайн, прежде чем приступать к производству.
- Если ваша основная цель — повышение эффективности производства: Обратите внимание на производственные вспомогательные средства. Печать нестандартных приспособлений и оснастки — это проверенная стратегия с высокой рентабельностью инвестиций для сокращения сроков выполнения и повышения качества процесса.
- Если ваша основная цель — создание высокопроизводительных продуктов: Детали конечного использования — ваша цель, но только если ваш дизайн требует сложной геометрии, снижения веса или индивидуализации, что оправдывает затраты.
В конечном итоге, лучшее применение аддитивного производства — это то, где его уникальные возможности решают конкретную инженерную или бизнес-задачу, которую не могут решить другие методы.
Сводная таблица:
| Этап применения | Основной вариант использования | Ключевые отрасли |
|---|---|---|
| Быстрое прототипирование | Итерация дизайна и тестирование посадки | Все отрасли |
| Производственные вспомогательные средства | Приспособления, оснастка и нестандартный инструментарий | Автомобильная, Промышленная |
| Производство деталей конечного использования | Функциональные, критически важные компоненты | Аэрокосмическая, Медицинская, Стоматологическая |
Готовы использовать аддитивное производство для своих производственных нужд? KINTEK специализируется на предоставлении передового лабораторного оборудования и расходных материалов, которые поддерживают весь рабочий процесс АП, от прототипирования до производства конечных деталей. Независимо от того, работаете ли вы в аэрокосмической, медицинской или автомобильной промышленности, наши решения могут помочь вам достичь сложной геометрии, консолидации деталей и массовой индивидуализации. Свяжитесь с нами сегодня, чтобы обсудить, как мы можем улучшить ваши возможности аддитивного производства!
Визуальное руководство
Связанные товары
- Цилиндрическая пресс-форма Assemble Lab
- Оборудование для стерилизации VHP Пероксид водорода H2O2 Стерилизатор пространства
- Оборудование для осаждения из паровой фазы CVD Система Камерная Печь-труба PECVD с Жидкостным Газификатором Машина PECVD
- Лабораторная вибрационная просеивающая машина с вибрационным ситом
- Система ВЧ-PECVD Радиочастотное плазменно-усиленное химическое осаждение из газовой фазы ВЧ-PECVD
Люди также спрашивают
- Есть ли разница в качестве выращенных в лаборатории бриллиантов? Да, и вот как определить лучшие
- Какой метод наиболее часто используется для синтеза наноматериалов? Руководство по доминирующим технологиям
- Каково применение торрефикации? Превращение биомассы в высокоэнергетический «биоуголь»
- Какова роль тонких пленок в устройствах? Невидимый двигатель современных технологий
- Могут ли углеродные нанотрубки образовываться естественным путем? Да, и вот где природа их создает.
- Каковы движущие силы спекания? Понимание термодинамики для создания лучших материалов
- Как лаборатории могут обеспечить оптимальную работу своих морозильных камер сверхнизких температур (ULT) с течением времени? Руководство по проактивному техническому обслуживанию
- Каков источник рентгеновского излучения? Сравнение рентгеновских трубок и радиоизотопов для анализа













