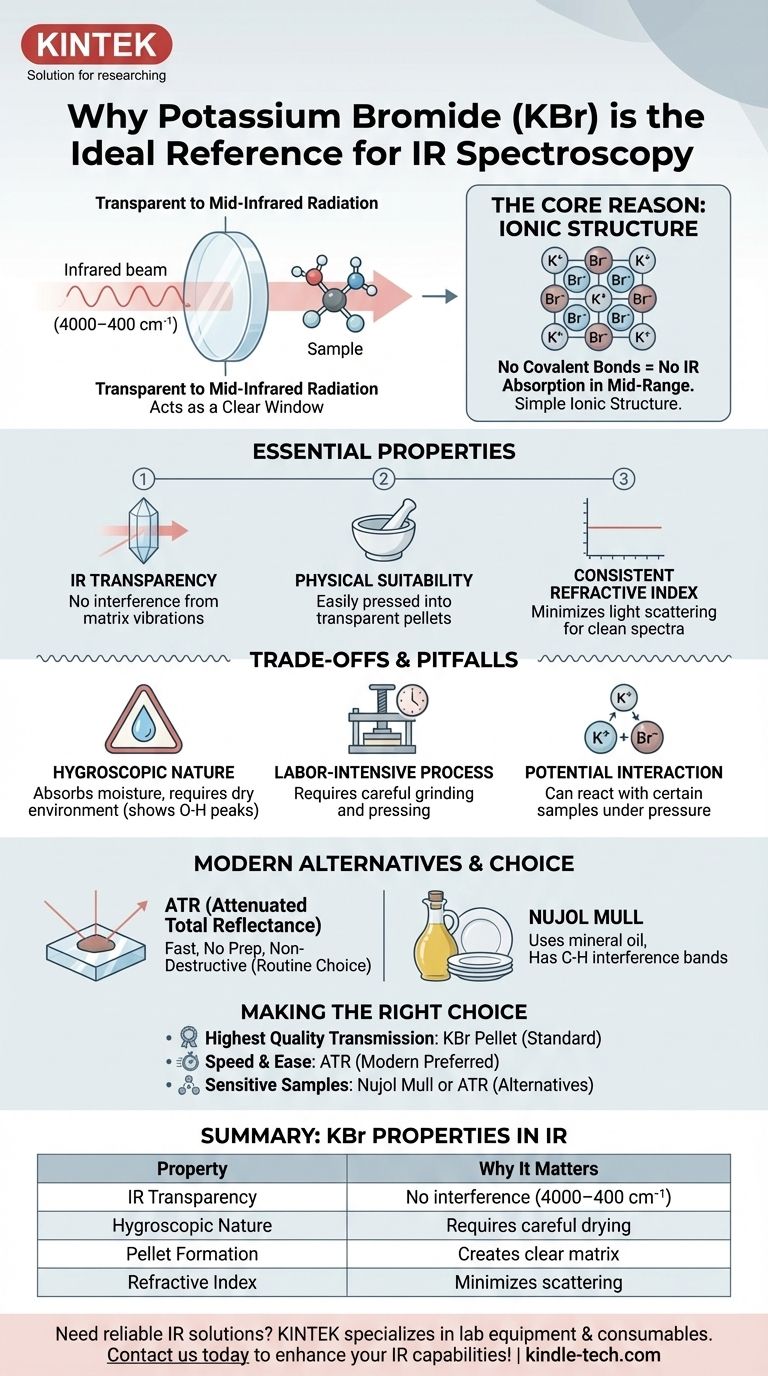
Коротко говоря, бромид калия (KBr) используется в качестве эталонного соединения и матрицы образца в ИК-спектроскопии, потому что он прозрачен для инфракрасного излучения. Его простая ионная структура не имеет молекулярных колебаний, которые поглощают энергию в типичном среднеинфракрасном диапазоне (4000–400 см⁻¹). Это уникальное свойство позволяет ему действовать как прозрачное «окно», удерживая исследуемый образец, чтобы спектрометр мог измерять спектр образца без помех.
Основная причина использования KBr заключается в отсутствии у него ковалентных связей, что означает отсутствие молекулярных колебаний, поглощающих свет в среднеинфракрасном диапазоне. Эта оптическая прозрачность позволяет спектрометру измерять спектр образца без помех от окружающего материала.

Основные свойства ИК-матрицы
Чтобы понять, почему KBr является традиционным выбором, необходимо понять, что делает любой материал пригодным для удержания образца для ИК-анализа. Идеальный материал не должен мешать самому измерению.
Принцип ИК-прозрачности
Инфракрасная спектроскопия работает путем измерения поглощения ИК-света ковалентными связями внутри молекулы, что вызывает их колебания (растяжение, изгиб и т. д.).
KBr — это ионная соль (K⁺Br⁻). Она не содержит ковалентных связей. Из-за этого у нее нет молекулярных колебаний, которые могут быть возбуждены среднеинфракрасным излучением, что делает ее фактически невидимой для спектрометра в наиболее полезной аналитической области.
Физическая пригодность для подготовки образцов
KBr — относительно мягкая кристаллическая соль. При измельчении в мелкий порошок и воздействии высокого давления (несколько тонн) кристаллы деформируются и слипаются.
Этот процесс создает тонкий, полупрозрачный или прозрачный твердый диск, часто называемый таблеткой KBr. Образец, который был измельчен вместе с KBr, оказывается заключенным в эту твердую, солевую матрицу, что делает его идеальным для анализа.
Постоянный показатель преломления
Хорошо приготовленная таблетка KBr имеет однородный показатель преломления, что помогает минимизировать рассеяние инфракрасного света. Это уменьшение рассеяния приводит к более плоской базовой линии и более чистому, более интерпретируемому спектру.
Понимание компромиссов и распространенных ошибок
Хотя KBr является традиционным стандартом, он не лишен проблем. Осознание этих ограничений критически важно для получения высококачественных данных.
Проблема поглощения воды
Наиболее существенным недостатком KBr является то, что он гигроскопичен, то есть легко поглощает влагу из атмосферы.
Вода (H₂O) имеет очень сильные, широкие полосы поглощения в ИК-диапазоне, особенно колебания растяжения O-H около 3400 см⁻¹. Если ваш KBr не хранится в абсолютно сухом состоянии, эти пики воды могут маскировать важные особенности спектра вашего образца.
Трудоемкий процесс
Создание высококачественной таблетки KBr требует тщательности, умения и времени. Образец и KBr должны быть измельчены в чрезвычайно мелкий порошок для уменьшения рассеяния света, гомогенно смешаны и тщательно спрессованы для создания прозрачной, нетреснувшей таблетки.
Потенциальное взаимодействие с образцом
Для некоторых типов образцов, таких как некоторые неорганические соли, существует риск реакции ионного обмена с матрицей KBr под давлением. Это может изменить образец и привести к неточному спектру.
Современные альтернативы методу KBr
Достижения в приборостроении предоставили мощные альтернативы, которые обходят проблемы, связанные с таблетками KBr.
Нарушенное полное внутреннее отражение (НПВО/ATR)
ATR в настоящее время является наиболее распространенным методом ИК-анализа твердых веществ и жидкостей. Он практически не требует подготовки образца.
Образец просто прижимается к кристаллу с высоким показателем преломления (часто алмазу или селениду цинка). ИК-луч отражается внутри кристалла, и небольшая часть его энергии проникает в образец, генерируя спектр. Этот метод быстрый, простой и неразрушающий.
Суспензия в нуйоле (Nujol Mull)
Более старая техника включает измельчение твердого образца с несколькими каплями минерального масла (нуйола) для создания густой пасты или суспензии. Затем эта паста распределяется между двумя солевыми пластинами (которые могут быть изготовлены из KBr или NaCl).
Основной недостаток заключается в том, что само минеральное масло имеет полосы поглощения C-H, которые всегда будут присутствовать в спектре, потенциально маскируя части «отпечатка пальца» образца.
Правильный выбор для вашего анализа
Выбор правильной методики подготовки образца полностью зависит от вашего образца, вашего оборудования и вашей аналитической цели.
- Если ваша основная цель — получение высококачественного, классического спектра пропускания для твердого образца: Метод таблеток KBr, при правильном выполнении в сухой среде, остается золотым стандартом.
- Если ваша основная цель — скорость, простота использования и минимальная подготовка образца: Нарушенное полное внутреннее отражение (ATR) почти всегда является превосходным современным выбором для рутинного анализа.
- Если ваш образец чувствителен к давлению или может реагировать с KBr: Рассмотрите метод суспензии в нуйоле или ATR как более безопасные альтернативы.
Понимание принципов, лежащих в основе выбора матрицы, позволяет вам генерировать чистые, надежные и интерпретируемые спектроскопические данные.
Сводная таблица:
| Свойство | Почему это важно для ИК-спектроскопии |
|---|---|
| ИК-прозрачность | Отсутствие ковалентных связей = отсутствие помех в диапазоне 4000–400 см⁻¹ |
| Гигроскопичность | Поглощает влагу, требуя тщательной сушки для предотвращения появления водяных пиков |
| Формирование таблеток | Создает прозрачную матрицу для твердых образцов под давлением |
| Показатель преломления | Минимизирует рассеяние света для более чистых базовых линий |
Нужны надежные решения для ИК-спектроскопии? KINTEK специализируется на лабораторном оборудовании и расходных материалах для точной подготовки и анализа образцов. Независимо от того, нужны ли вам таблетки KBr, аксессуары ATR или экспертное руководство для оптимизации ваших спектроскопических результатов, наши продукты обеспечивают точность и эффективность для вашей лаборатории. Свяжитесь с нами сегодня, чтобы обсудить ваши конкретные потребности и улучшить ваши возможности в ИК-спектроскопии!
Визуальное руководство
Связанные товары
- Машина для заливки металлографических образцов для лабораторных материалов и анализа
- Автоматический гидравлический пресс с подогревом и нагревательными плитами для лабораторного горячего прессования 25Т 30Т 50Т
- Одноштамповочный электрический таблеточный пресс Лабораторный порошковый таблеточный пресс TDP
- Ручной высокотемпературный гидравлический пресс с нагревательными плитами для лаборатории
- Машина для холодного изостатического прессования CIP для производства небольших заготовок 400 МПа
Люди также спрашивают
- Что такое запрессовка в металлургии? Руководство по идеальной подготовке образцов
- Как следует устанавливать образец на держатель образца? Обеспечьте механическую стабильность и электрическую целостность
- Какова общая процедура и какие меры предосторожности следует соблюдать во время процесса полировки? Достижение безупречной отделки электрода
- Какую роль играют лабораторные системы шлифовки и полировки в азотировании? Обеспечение превосходной зеркальной поверхности и проникновения ионов
- Какова разница между горячим и холодным прессованием образцов? Выберите правильный метод для вашего образца



















